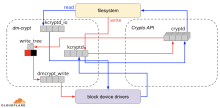
Encrypting a Linux volume with cryptsetup involves a few steps. Here's a basic guide:
Install cryptsetup: If it's not already installed on your Linux system, you can install it using your package manager. For example, on Ubuntu or Debian, you can use:
sudo apt-get install cryptsetupPartition the disk: If the disk isn't already partitioned, you'll need to do that first. You can use tools like fdisk or parted for this purpose.